- Seismics
- Coring Equipment
- Sediment physics
- Sediment chemistry
- Process rates
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Water column
Methane concentration
Sulfate concentration
Sulfide concentration
Stable isotopes: 12C/13C analysis of CH4 and CO2
Total Organic Carbon / Nitrogen (TOC / TN)
DIC, Dissolved Inorganic Carbon
Volatile fatty acids (VFA) and sulfate in porewater samples
Pyrite, iron sulfide, elemental sulfur
Reactive iron
210Pb, 137Cs
Methane concentration
| Take a sediment sample of exactly 3 ml with a 5 ml (or 3 ml) syringe with the luer tip removed. |
| Transfer the sample to a 20 ml serum vial containing 6 ml NaOH (2.5 %) or 6 ml milli-Q H2O 1). Close the vial immediately with a rubber stopper and an aluminum crimp seal. |
| The gas peaks are integrated by an integrator (Hewlett Packard 3395). Methane elutes at 0.65 min. |
| The concentration is calculated from the integrated area (A) of the methane peak by
comparison with a standard curve (based on 100 ppmV and 1000 ppmV methane standards) and corrected for background. |
Calculation of the CH4 concentration expressed as amount per volume sediment:
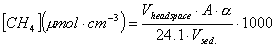
1) Effects of sample treatment with H2O instead of NaOH on the measured CH4 concentration were investigated in various test series applying sample storage times of a few hours up to 0.5 y. Differences of measured CH4 concentrations between H2O treatments and NaOH controls were never observed.
back to top